 As an indispensable part of modern industry and commercial activities, remote cooling systems play an important role in terms of energy efficiency and sustainability as well as keeping products fresh. Remote cooling systems, especially for the preservation of sensitive products such as wine cellars, are becoming increasingly effective and environmentally friendly with advances in technology.
As an indispensable part of modern industry and commercial activities, remote cooling systems play an important role in terms of energy efficiency and sustainability as well as keeping products fresh. Remote cooling systems, especially for the preservation of sensitive products such as wine cellars, are becoming increasingly effective and environmentally friendly with advances in technology.
Remote cooling systems are often used in large storage facilities, supermarkets, restaurants and hotels. These systems use a refrigeration unit or system outside to keep the temperature inside under control. This allows more space to be utilized indoors and maintain the desired temperature range.
Remote cooling systems specifically designed for wine cellars precisely control the temperature and humidity level to ensure optimum storage conditions for the wine. These systems reduce costs for businesses by saving energy while maintaining the quality of the wine.
Compared to traditional cooling systems, remote cooling systems offer a number of advantages. These include lower energy consumption, less maintenance, less noise and longer lifetime. Furthermore, remote cooling systems can use environmentally friendly refrigerants to reduce environmental impact, which is an important step towards sustainability.
There are remote cooling systems specifically designed for the preservation of sensitive products such as wine cellars. These systems provide optimum storage conditions for wine by precisely controlling temperature and humidity levels. In addition, remote cooling systems generally consume less energy, require less maintenance, produce less noise and have a longer lifespan. With these features, they help businesses reduce costs while also reducing environmental impact.
Cooling Unit: This is a unit located outside that removes heat, usually through air or water. The refrigeration unit includes a compressor, a condenser and a fan, which are used to lower the temperature indoors.
Evaporator: Located indoors, the evaporator lowers the temperature through evaporation of the refrigerant. This allows air or water indoors to be cooled.
Refrigerant: This is a special fluid used to transfer heat. The refrigerant transfers temperature as it circulates between the refrigeration unit and the evaporator.
The principle of operation is usually as follows:
The refrigerant is compressed in the refrigeration unit and turned into a liquid.
This liquid refrigerant is released under low pressure on its way to the evaporator.
The refrigerant under this low pressure in the evaporator evaporates, taking heat from the environment and lowering the temperature indoors.
The evaporated refrigerant returns back to the refrigeration unit and completes the cycle.
This cycle continues continuously, thus keeping the indoor temperature at the desired level. In this way, remote cooling systems keep the interior cool and help keep products fresh.

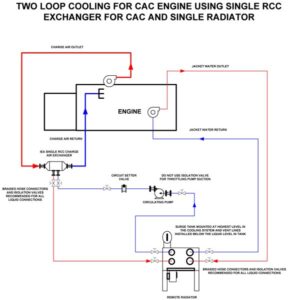
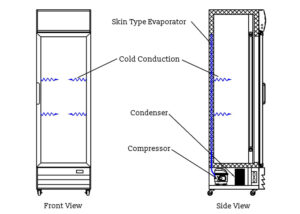 The engine assembly is an important component for the refrigeration system on a cabinet. This system usually includes a fan, a refrigeration compressor, a condenser (heat exchanger) and an evaporator (heat sink). The fan circulates air inside the cabinet and exhausts hot air to the outside. The refrigeration compressor sucks in the low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator, compresses it and pushes the high-pressure hot gas into the condenser. The condenser allows the gas to give off heat and turn into liquid. The evaporator receives the liquid refrigerant stream, evaporates it and reduces the temperature in the process, thus cooling the inside of the cabinet. These systems usually use liquid refrigerant (usually R134a, such as R449a) and are powered by electricity.
The engine assembly is an important component for the refrigeration system on a cabinet. This system usually includes a fan, a refrigeration compressor, a condenser (heat exchanger) and an evaporator (heat sink). The fan circulates air inside the cabinet and exhausts hot air to the outside. The refrigeration compressor sucks in the low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator, compresses it and pushes the high-pressure hot gas into the condenser. The condenser allows the gas to give off heat and turn into liquid. The evaporator receives the liquid refrigerant stream, evaporates it and reduces the temperature in the process, thus cooling the inside of the cabinet. These systems usually use liquid refrigerant (usually R134a, such as R449a) and are powered by electricity.